Startup Law

In Turkey, startup is a recently growing business model concept. It is possible to consider this concept as follows: An entrepreneur, who started with an idea from the zero point, conducts his businesses by incorporating a company. After new ideas take shape in the entrepreneur’s mind within the framework of technological developments and social needs, it will be possible for such ideas to be put into practice, if the necessary investments can be provided. However, at this point, the matters necessary to be addressed are the basic problems such as how a new idea shall be protected, assessment of the startup in respect of the entrepreneur and the investor and how should the company be incorporated. At this point, “the Startup Law” comes into our lives as a new concept.
The Startup (Entrepreneurship) Law is qualified as a new branch of law, which incorporates Information Technology Law, Companies Law and Intellectual Property Law and has emerged by the effect of the entrepreneurship sector. Since initiatives are directly interacting with the legal rules of the fields in which they operate, the scope of the Entrepreneurship Law is expanding gradually. Once the field, in which initiatives can take place, has no boundaries; E-Commerce Law, Labor Law, Personal Data Protection Law and Taxation Law also become automatically a part of the lives of those dealing with this field.
Roadmap for entrepreneurs
Since the born of a new idea is included in entrepreneurship, a number of legal phases come into question, apart from the ideational phases prior to the implementation of such initiative. These legal phases start from the imitation of an idea to the enforcement of the Intellectual Property Law for the protection of the idea and incorporate Information Technology Law, Contracts Law and Personal Data Protection Law and come to an end with the implementation of Commercial Law by the sale of the idea at the sale stage or by the incorporation of a new company or sometimes by investor companies’ acquisitions of shares.
How can I protect my new idea?
The thought of finding a new idea is exciting and also brings about many considerations such as whether or not such idea is unique, how such idea shall be protected, whether or not it is really possible to put such idea into practice and whether or not it will be possible to provide the necessary investment. Within this scope, we will touch upon briefly below the basic protection systems in Turkish Law within the context of the concepts of trademark, patent and utility model as part of the Intellectual Property Code.
Trademarks
The main function of a trademark is to ensure that the goods or services of an enterprise are distinguished from the goods or services of another enterprise. After the right to trademark is obtained, registration is not mandatory; however, upon registration, it provides a number of protections with its owner. For entrepreneurs, such registration and protection provided by the right to trademark may be of great importance in order to prevent the emerge of competitors under the same or different names after the entrepreneurs start providing to their target groups their goods or services they produced for the first time and after they succeed in this regard.
Trademark registration process and trademark registration
Trademark applications are first examined in terms of form. The examination in terms of form consists of looking into whether or not there is a lacking document or an error. After the examination in terms of form is completed, another examination is carried out on whether or not there are any absolute grounds of refusal pursuant to the article 5 of the Industrial Property Code. In cases where it is not possible register the sign as a trademark, the application is refused with regard to all or a part of the goods and services for which the registration is requested. In the absence of the absolute grounds of refusal and in case there is no deficiency in terms of form with respect to the application conditions, the relevant trademark application is published in the Official Trademarks Bulletin. After publication in the Bulletin, third parties may object to those trademarks within 2 months as from the publication date.
If a trademark, for which registration request is submitted, is already registered in the name of another person; such new trademark application shall not be refused in case of submission of a document indicating that the owner of the earlier trademark expressly grants consent to the registration of the application, and this circumstance will constitute an exception to the absolute grounds of refusal.
Trademark registration process
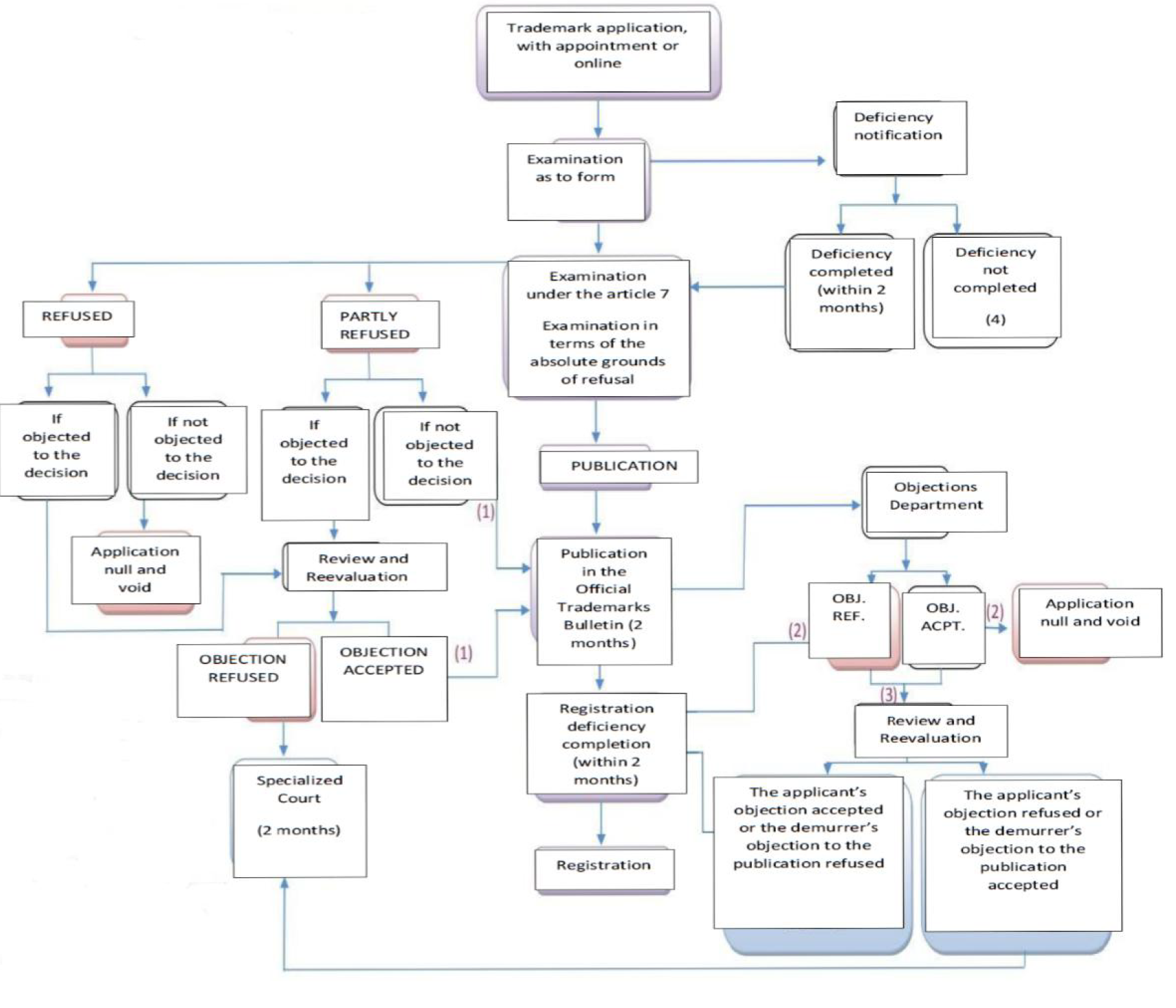
Notes:
(1) Publication in the Official Trademarks Bulletin, for the goods published.
(2) In case an objection is not submitted against the decision within 2 months.
(3) In case an objection is submitted against the decision within 2 months.
(4) In case such deficiency is not completed within 2 months, the deficiency-related requests are not taken into consideration or such applications become null and void pursuant to the provisions of the legislation.
Patents
The right to patent shall arise in the case that a person develops an idea bearing the characteristics of invention and that this fact does not bear a matter constituting an impediment against registration. There is 1-year statute of limitations period as from the date when it is announced to the public that the right to patent has arisen. If the relevant application is not filed with the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office within this 1-year term, the right to patent will be lost. A patent is not granted to every invention. The following are the matters and inventions that are not patentable:
- Scientific theory, discovery and math methods;
- Plans, procedures and rules regarding mental, commercial and game activities;
- Computer software, creations with literary work, art work, science work, aesthetic characteristic;
- Procedures with no technical aspects related to information compilation, arrangement, presentation and transmission;
- Surgical and treatment methods that will be applied to human or animal body and diagnostic procedures related to human, animal body.
As can be understood, our legislation expressly states that any computer software is not patentable. However, this might consequently cause the software to be left unprotected. Therefore, it is possible to be a copyright holder on computer software.
For patents, there are two types of registration systems as “without examination” and “with examination”. Both systems will provide a protection period of three years, if those patents are granted registration. The protection period of an application made without examination is seven years as from the application date. At the end of seven years, the product or method relevant to the invention becomes anonymous and the right to patent terminates. However, the protection period is twenty years in the system with examination.

Business model registration (utility models)
Utility model is defined as a concept whereby the owners of the inventions that are new and with industrial applicability are granted the right to produce and market their products relevant to the invention within a period of ten years. Utility model is a certificate which has an economic value and grants an exclusive right to the person that has made the invention and thus, provides protection on the basis of his invention for a certain period of time in exchange for disclosing his invention to the public. Before submitting a utility model application, an investigation should be carried out for the relevant invention in terms of the conditions required for the grant of utility model.

A utility model certificate is more convenient in terms of both cost and time savings, compared to a patent certificate, and is ideal for small-scale enterprises to put their inventions into practice. Against acts of infringement, utility model protection is regulated so as to be applied to the life quicker than patent protection. In our Country, utility model applications are filed with the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office, and the application phases will take place as follows:
- After the necessary application fee is paid, the application will be submitted before the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office. Then, the utility model specialists in charge will examine the application in terms of form.
- The relevant search report will be prepared. This report represents the first stage in deciding whether or not the invention is registerable. After the search report, the relevant examination report will be prepared upon the applicant’s request.
- For an application that is determined to be registrable in result of the search report, the applicant will pay the relevant fee and then, may request that the utility model certificate be issued and that the utility model be registered.
- In principle, the application will be published after 18 months have elapsed from the application date. However, in the application form filled up while submitting the utility model application, if the applicant has filled in the section related to early publication; or if the applicant has made the request together with an Early Publication Request Form in the subsequent process, the applicant may request that the application be published before 18 months elapse.
- In case the search report is completed before the application is published, the search report will be published together with the application. If the search report has been prepared after the application is published, the search report will be published separately from the application.
- The purpose of the publication of the application is to ensure that third parties can apply for the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office in respect of whether utility model may be granted to the invention constituting the subject of the utility model application.

Company incorporation phase
For entrepreneurs, the company incorporation phase should be carried out in such a way that it will be completed by incurring a minimum amount of expenses and then, in such a way that it will create the least liability. Within this context, an entrepreneur may prefer unlimited companies as general partnership or partnership in commendam, or stock corporations as limited liability company or joint stock company. In terms of liability, we are of the opinion that it will be more appropriate to put the startup into practice through incorporation of a stock corporation rather than an unlimited company. We will briefly touch upon the advantages about stock corporations.
For limited liability companies
The amount of the expenses that will be incurred in the course of incorporating a limited liability company varies depending on the number of shareholders, the amount of the capital and the number of managers. The mentioned capital amount should be completed by the shareholders within 2 years, without causing the bank to block a portion of this amount. The liability of the shareholders is only limited to the payment of the principal capital amount they commit and does not cover the corporate debts.
However, the following provision is contained in the Law on Collection Procedure of Public Receivables: “The shareholders of a limited liability company shall be directly, but in proportion to their capital shares, liable for the public receivables not possible to be collected from the company, and enforcement proceedings shall be carried out against the shareholders as required by the provisions of this Law”. Even if it is thought that the shareholders do not have a liability since it is a stock corporation, the shareholders will therefore have a direct liability pursuant to the above provision. For an entrepreneur, it is possible to say that the above provision will have disadvantage since it may create such liability.
For joint stock companies
In terms of cost, it is more disadvantageous to incorporate a joint stock company, compared to a limited liability company. This is because; after having blocked in a bank one-fourth of the principal capital committed in the course of incorporating a joint stock company, the remaining amount must be completed within 2 years. However; for a limited liability company, it is not necessary to block an amount in a bank.
As regards the liability of shareholders, the shareholders are only liable for the principal capital shares they commit. Therefore, there is relatively a more advantageous circumstance than a limited liability company. In a joint stock company, the board of directors shall be liable only if they are in breach of their obligations through their faults, which obligations arise from the laws or the company articles of association. For an entrepreneur, a joint stock company may seem like quite costly in terms of the incorporation expenses and the company’s fixed overheads. However; in case such entrepreneur’s initiative ends up adversely, a joint stock company will ensure that the entrepreneur recovers from this situation with the least liability. Likewise, since a tax exemption applies to joint stock companies, the relevant income tax will not be paid in case of a share certificate or an interim certificate in print.

In our newsletter, we have drawn a road map for entrepreneurs and addressed in legal aspects the matter “in case a person has a new idea, how he may protect and develop this idea”. Taking into consideration the relevant advantages and disadvantages in respect of his idea, an entrepreneur will prefer a way which will keep him out of liability and whereby he will be able to develop his idea the most unshakably. By the reason that the matter is intertwined with many branches of law and has many phases, it will be possible to ensure such development more easily through the facilitation of the process by means of consulting and receiving legal support from specialist lawyers.